File:Trajectories-of-the-Earth-System-Anthropocene-Pathway-of-Earth-System-Holocene.jpg
Trajectories-of-the-Earth-System-Anthropocene-Pathway-of-Earth-System-Holocene.jpg (798 × 522 pixels, file size: 78 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
Summary
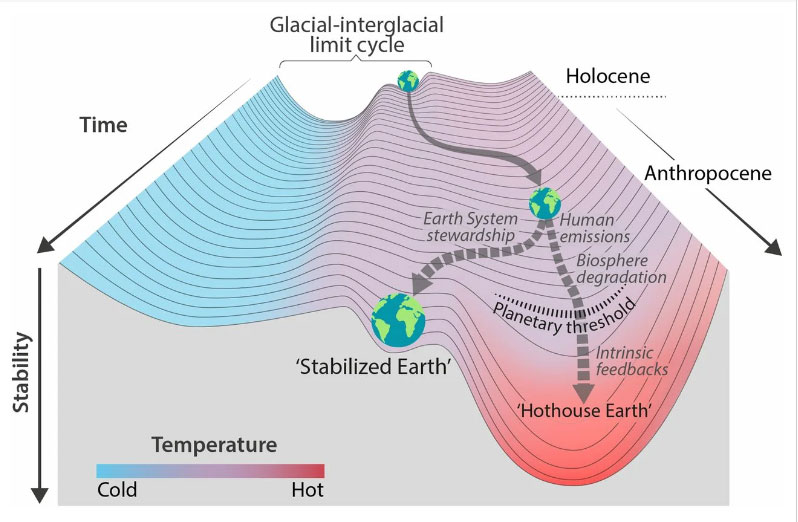
Stability landscape showing the pathway of the Earth System out of the Holocene and thus, out of the glacial–interglacial limit cycle to its present position in the hotter Anthropocene. The fork in the road in Fig. 1 is shown here as the two divergent pathways of the Earth System in the future (broken arrows). Currently, the Earth System is on a Hothouse Earth pathway driven by human emissions of greenhouse gases and biosphere degradation toward a planetary threshold at ∼2 °C (horizontal broken line at 2 °C in Fig. 1), beyond which the system follows an essentially irreversible pathway driven by intrinsic biogeophysical feedbacks. The other pathway leads to Stabilized Earth, a pathway of Earth System stewardship guided by human-created feedbacks to a quasistable, human-maintained basin of attraction. “Stability” (vertical axis) is defined here as the inverse of the potential energy of the system. Systems in a highly stable state (deep valley) have low potential energy, and considerable energy is required to move them out of this stable state. Systems in an unstable state (top of a hill) have high potential energy, and they require only a little additional energy to push them off the hill and down toward a valley of lower potential energy. Source: https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.1810141115
(C) National Academy of Science
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 10:25, 12 May 2023 |  | 798 × 522 (78 KB) | Chris (talk | contribs) | Stability landscape showing the pathway of the Earth System out of the Holocene and thus, out of the glacial–interglacial limit cycle to its present position in the hotter Anthropocene. The fork in the road in Fig. 1 is shown here as the two divergent pathways of the Earth System in the future (broken arrows). Currently, the Earth System is on a Hothouse Earth pathway driven by human emissions of greenhouse gases and biosphere degradation toward a planetary threshold at ∼2 °C (horizontal brok... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: